Chapter 14: Personal Care and Healthy Behaviors
Terms to know: epidermis, dermis, melanin, sebaceous gland, sweat glands, melanoma, hair follicle, dandruff, periodontium, pulp, plaque, periodontal disease, tartar, lacrimal gland, sclera, cornea, choroid, retina, external auditory canal, auditory ossicles, labyrinth, tinnitus
I. Healthy Skin, Hair and Nails
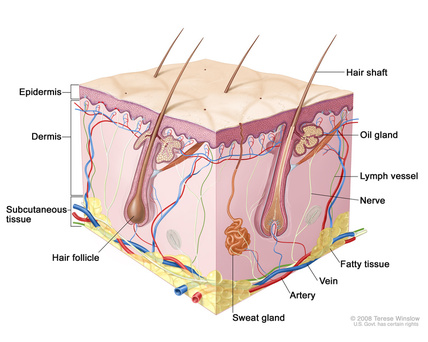
A. Structure and Function of the Skin -
1. Epidermis - the outer, thinner layer of skin that is composed of living and dead
cells.
2. Dermis - the thicker layer of the skin that is beneath the epidermis that is
made up of connective tissue and contains blood vessels and nerves
3. Melanin - pigment that gives the skin, hair, and iris of the eye their color
** less melanin means more risk of damage from UV rays**
4. Sebaceous Glands - produces oily secretion called SEBUM (keeps the skin
from drying out)
5. Sweat Glands - within the dermis, these glands secrete perspiration through
ducts to pores on the skins surface
B. Keeping Healthy Skin
1. Daily Washing removes growth of bacteria that causes body odor
2. avoid touching your face with your hands (quickest way to introduce bacteria
into your body)
3. Keep skin moisturized to prevent irritations
4. follow a diet rick in vitamins and minerals.....especially vitamin A
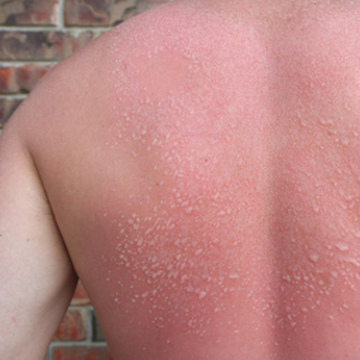
C. Effects of the Sun
1. Increased production of melanin causes people to become tan (this is the bodys way to protect cells from UV rays)
2. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation causes
a. formation and growth of cancerous cells
b. breaks down elastic fibers that support the skin
c skin will wrinkle or become hard and leathery
1. Epidermis - the outer, thinner layer of skin that is composed of living and dead
cells.
2. Dermis - the thicker layer of the skin that is beneath the epidermis that is
made up of connective tissue and contains blood vessels and nerves
3. Melanin - pigment that gives the skin, hair, and iris of the eye their color
** less melanin means more risk of damage from UV rays**
4. Sebaceous Glands - produces oily secretion called SEBUM (keeps the skin
from drying out)
5. Sweat Glands - within the dermis, these glands secrete perspiration through
ducts to pores on the skins surface
B. Keeping Healthy Skin
1. Daily Washing removes growth of bacteria that causes body odor
2. avoid touching your face with your hands (quickest way to introduce bacteria
into your body)
3. Keep skin moisturized to prevent irritations
4. follow a diet rick in vitamins and minerals.....especially vitamin A
C. Effects of the Sun
1. Increased production of melanin causes people to become tan (this is the bodys way to protect cells from UV rays)
2. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation causes
a. formation and growth of cancerous cells
b. breaks down elastic fibers that support the skin
c skin will wrinkle or become hard and leathery
D. Protecting the skin
1. Always wear sunscreen on exposed areas of your skin
a. use an spf or higher and make sure it blocks UVA and UVB
b. apply 15 to 30 minutes before going outside even on cloudy days
2. Wear protective clothing:
a. hats, long sleeve shirts, long pants and sunglasses
b. Sun is most intense between 10:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m.
E. Skin Problems
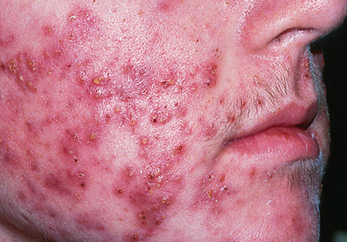
1. Acne - caused when pores in the skin get clogged and the sebum produced by the sebaceous glands cant reach the skins surface
a. wash face gently twice daily and apply over the counter creams
b. touching or picking at it only aggravates the condition and may cause scarring
c. is not caused by greasy foods or eating chocolate
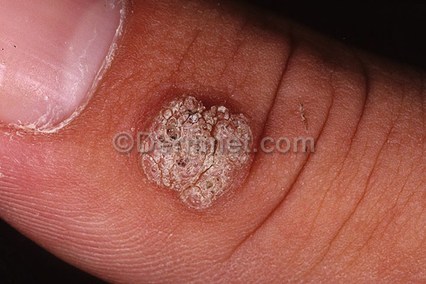
2. Warts - caused by a virus. non cancerous growths that can appear anywhere on the body. come from contact with infected skin
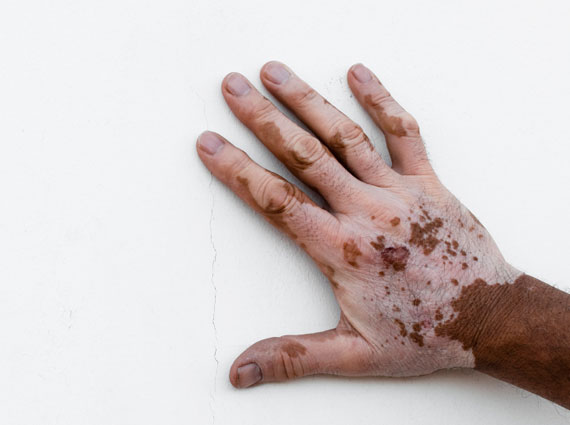
3. Vitiligo - patches of skin lose their pigment (Michael Jackson)
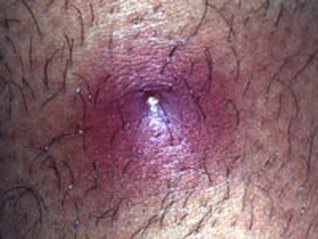
4. Boils - form when hair follicles become infected and become inflamed and pus forms. NEVER SQUEEZE OR BURST!!!
1. Acne - caused when pores in the skin get clogged and the sebum produced by the sebaceous glands cant reach the skins surface
a. wash face gently twice daily and apply over the counter creams
b. touching or picking at it only aggravates the condition and may cause scarring
c. is not caused by greasy foods or eating chocolate
2. Warts - caused by a virus. non cancerous growths that can appear anywhere on the body. come from contact with infected skin
3. Vitiligo - patches of skin lose their pigment (Michael Jackson)
4. Boils - form when hair follicles become infected and become inflamed and pus forms. NEVER SQUEEZE OR BURST!!!
Acne
Warts
Vitiligo
BOILS
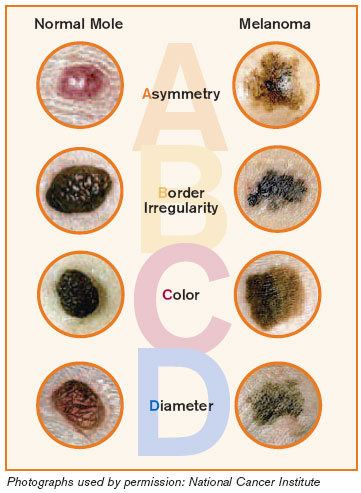
F. ABCD"S of Melanoma (MOST SERIOUS FORM OF SKIN CANCER)
A ASYMMETRY - draw an imaginary line through the center of the mole. Both sides should be equal
B BORDER IRREGULARITY - non cancerous moles have smooth edges
C COLOR - look for moles that are intensely black or have a bluish tint
D DIAMETER - check for moles that are wider across than a pea
A ASYMMETRY - draw an imaginary line through the center of the mole. Both sides should be equal
B BORDER IRREGULARITY - non cancerous moles have smooth edges
C COLOR - look for moles that are intensely black or have a bluish tint
D DIAMETER - check for moles that are wider across than a pea
G. Hair
1. You have hair everywhere except the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet
2. your hair itself is composed of dead cells
3. hair follicle is the structure that surrounds the root of the hair
H. Hair "ISSUES"
1. Dandruff - a condition that can occur if the scalp becomes too dry and dead skin cells are shed as sticky
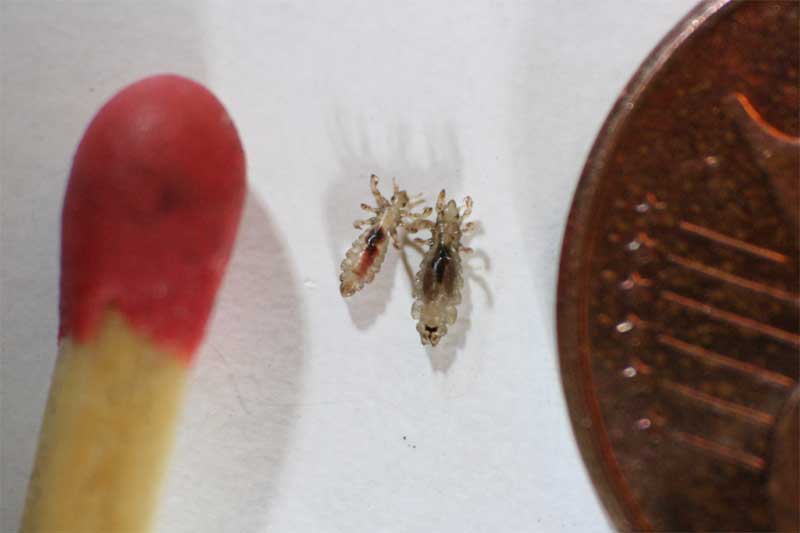
2. Head Lice - tiny parasites that infect and live in the scalp hair of humans. the feed on blood by biting through the skin of the scalp
1. You have hair everywhere except the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet
2. your hair itself is composed of dead cells
3. hair follicle is the structure that surrounds the root of the hair
H. Hair "ISSUES"
1. Dandruff - a condition that can occur if the scalp becomes too dry and dead skin cells are shed as sticky
2. Head Lice - tiny parasites that infect and live in the scalp hair of humans. the feed on blood by biting through the skin of the scalp
Dandruff
Head Lice
II. Care for the TEETH and MOUTH
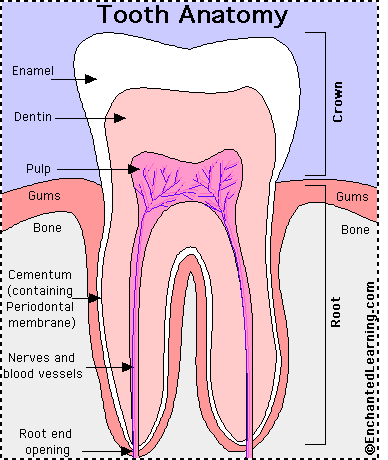
A. Periodontium - the area immediately around the teeth
B. Pulp - the tissue that contains the blood vessels and nerves of the tooth
C. Plaque- sticky colorless film that acts on sugar to form acids that destroy tooth enamel
and irritate gums
D. 5 tips to Effective Brushing -
1. hold the bristle tips at a 45 degree angle against the gumline
2. brush back and forth in short strokes. use a gentile scrubbing motion
3. brush the outer surfaces of each tooth, the inner surfaces then the chewing surfaces
4. to clean the inside surfaces of your front teeth, tilt the brush vertically and make up
and down strokes
5. floss only between the surface of each tooth but also beneath the gumline
E. FACTS
1. brushing after you eat removes the plaque that causes bacteria to produce the acid
that breaks down the enamel
2. Cavities are formed from this acid and need to be treated before reaching the pulp
3. Should see the dentist every 6 months for regular check-ups and cleaning
4. Follow a well-balanced diet that includes food containing phosphorus, calcium and
vitamin C
5. avoid all tobacco products
6. use fluoride products to help reduce tooth decay
F. Problems of the Teeth and Mouth
1. Halitosis - "Bad Breath" can be caused by eating certain foods or poor oral hygiene,
smoking, bacteria on the tongue or gum disease
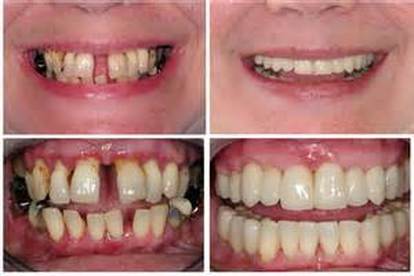
2. Tarter - "gingivitis" gums are irritated and swollen. The disease is reversible through
regular brushing and flossing.
3. Malocclusion - "bad bite"
4. Periodontal Disease - an inflammation of the periodontal structures caused by bacterial infection. Often called gum disease.
a. risk factors - smoking, diabetes, stress, medications, illness, genetics.
B. Pulp - the tissue that contains the blood vessels and nerves of the tooth
C. Plaque- sticky colorless film that acts on sugar to form acids that destroy tooth enamel
and irritate gums
D. 5 tips to Effective Brushing -
1. hold the bristle tips at a 45 degree angle against the gumline
2. brush back and forth in short strokes. use a gentile scrubbing motion
3. brush the outer surfaces of each tooth, the inner surfaces then the chewing surfaces
4. to clean the inside surfaces of your front teeth, tilt the brush vertically and make up
and down strokes
5. floss only between the surface of each tooth but also beneath the gumline
E. FACTS
1. brushing after you eat removes the plaque that causes bacteria to produce the acid
that breaks down the enamel
2. Cavities are formed from this acid and need to be treated before reaching the pulp
3. Should see the dentist every 6 months for regular check-ups and cleaning
4. Follow a well-balanced diet that includes food containing phosphorus, calcium and
vitamin C
5. avoid all tobacco products
6. use fluoride products to help reduce tooth decay
F. Problems of the Teeth and Mouth
1. Halitosis - "Bad Breath" can be caused by eating certain foods or poor oral hygiene,
smoking, bacteria on the tongue or gum disease
2. Tarter - "gingivitis" gums are irritated and swollen. The disease is reversible through
regular brushing and flossing.
3. Malocclusion - "bad bite"
4. Periodontal Disease - an inflammation of the periodontal structures caused by bacterial infection. Often called gum disease.
a. risk factors - smoking, diabetes, stress, medications, illness, genetics.
Gingivitis
Periodontal Disease
III. The Eye
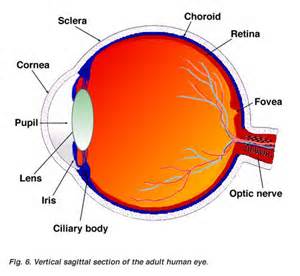
A. Parts of the Eye
1. Sclera - the tough white part of the eye
2. Cornea - transport tissue that bends and focuses light before it enters the lens
3. Choroid - thin structure that lines the inside of the sclera
4. Retina - the light-sensitive membrane on which images are cast by the cornea
B. Vision Problems
1. Astigmatism - irregular curvature of the cornea or lens and the eye is not able to
focus properly
2. Strabismus - muscles around the eye are weak which may cause the eye to be off-
center
3. Glaucoma - abnormally high pressure inside the eye causes damage to the retina and the
optic nerve and can result in loss of sight
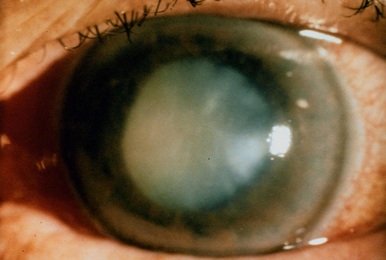
4. Cataracts - the lens becomes cloudy and can interfere with the lens's ability to focus
5. Muscular Degeneration - cells of the macula, opposite the lens begin to malfunction
1. Sclera - the tough white part of the eye
2. Cornea - transport tissue that bends and focuses light before it enters the lens
3. Choroid - thin structure that lines the inside of the sclera
4. Retina - the light-sensitive membrane on which images are cast by the cornea
B. Vision Problems
1. Astigmatism - irregular curvature of the cornea or lens and the eye is not able to
focus properly
2. Strabismus - muscles around the eye are weak which may cause the eye to be off-
center
3. Glaucoma - abnormally high pressure inside the eye causes damage to the retina and the
optic nerve and can result in loss of sight
4. Cataracts - the lens becomes cloudy and can interfere with the lens's ability to focus
5. Muscular Degeneration - cells of the macula, opposite the lens begin to malfunction
Glaucoma
Cataracts
IV. The Ear
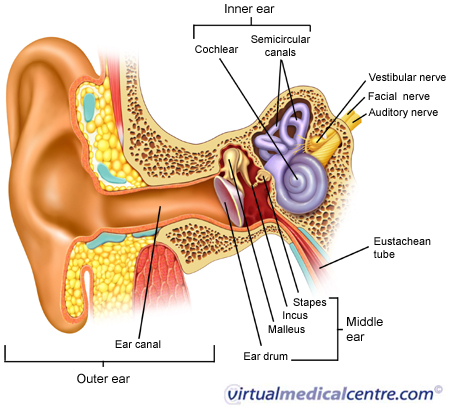
A. The 3 Parts of the Ear
1. The Outer Ear
- External Auditory Canal - passageway about one inch long that leads to
remaining portion of the ear
2. The Middle Ear
- Auditory Ossicles - three small bones linked together that connect the
eardrum to the inner ear
3. The Inner Ear
- Labyrinth - hearing and balance part of the ear
B. Problems of the Ear
1. Tinnitus - condition in which a ringing, buzzing, whistling, roaring, hissing or
other sound is heard in the ear in the absence of external sound
1. The Outer Ear
- External Auditory Canal - passageway about one inch long that leads to
remaining portion of the ear
2. The Middle Ear
- Auditory Ossicles - three small bones linked together that connect the
eardrum to the inner ear
3. The Inner Ear
- Labyrinth - hearing and balance part of the ear
B. Problems of the Ear
1. Tinnitus - condition in which a ringing, buzzing, whistling, roaring, hissing or
other sound is heard in the ear in the absence of external sound